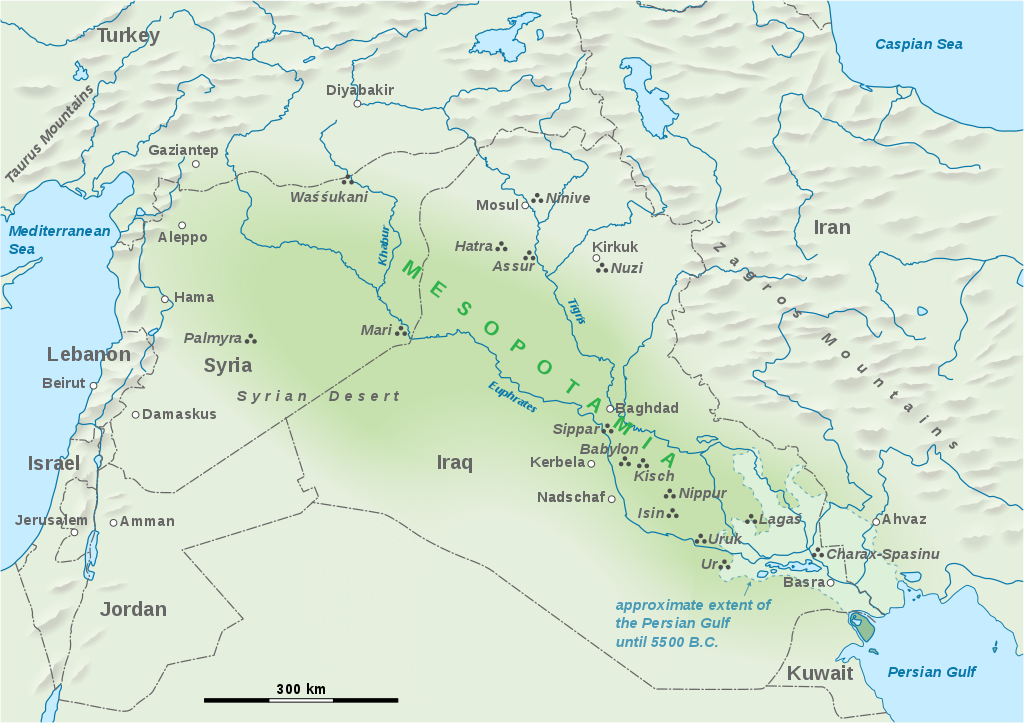
Mesopotamia, meaning “between two rivers” refers to a historical region in West Asia situated within the Tigris-Euphrates river system. It is often referred to as the cradle of civilization because it is where some of the most influential early city-states and empires first emerged. Mesopotamia encompasses modern-day Iraq, eastern Syria, southeast Turkey, parts of western Iran, and Kuwait.
Historical Significance
Mesopotamia is known for its significant contributions to human civilization. It was home to many different civilizations that spanned thousands of years and greatly influenced world culture and progress. Mesopotamia was home to ancient civilizations like Sumer, Assyria, and Babylonia, which influenced the development of mathematics and astronomy. Mesopotamia’s clay-based architecture and artifacts are distinctive features that reflect the civilization’s reliance on clay as a primary material. The area was also known for its urbanization, trade networks, and religious practices that shaped early societies.
Achievements and inventions that originated in Mesopotamia
- Writing: Mesopotamia is credited with the creation of the earliest known script called cuneiform.
- Mathematics: The concept of time, as well as mathematical advancements, were developed in Mesopotamia.
- Wheel: The wheel, a fundamental invention that revolutionized transportation, was first developed in Mesopotamia.
- Sailboats: Mesopotamians were skilled sailors and developed sailboats for transportation and trade.
- Maps: The concept of mapping and cartography was developed in Mesopotamia.
- Irrigation: Mesopotamians developed advanced irrigation systems to support agriculture and maximize crop yields.
- Civil Rights: Mesopotamia had early legal codes that recognized civil rights and established laws for society.
Civilization and Empires
Mesopotamia was home to various civilizations and empires that left a lasting impact on the region and beyond. Some of the notably;
- Sumerians
The Sumerians were one of the earliest civilizations in Mesopotamia and made significant contributions to writing, city-building, and art.
- Assyrians
The Assyrians rose to power and established a powerful empire in Mesopotamia, known for their military prowess and advanced administrative systems.
- Babylonians
The Babylonians, under the rule of Hammurabi, created a centralized bureaucracy and implemented a code of laws known as the Code of Hammurabi
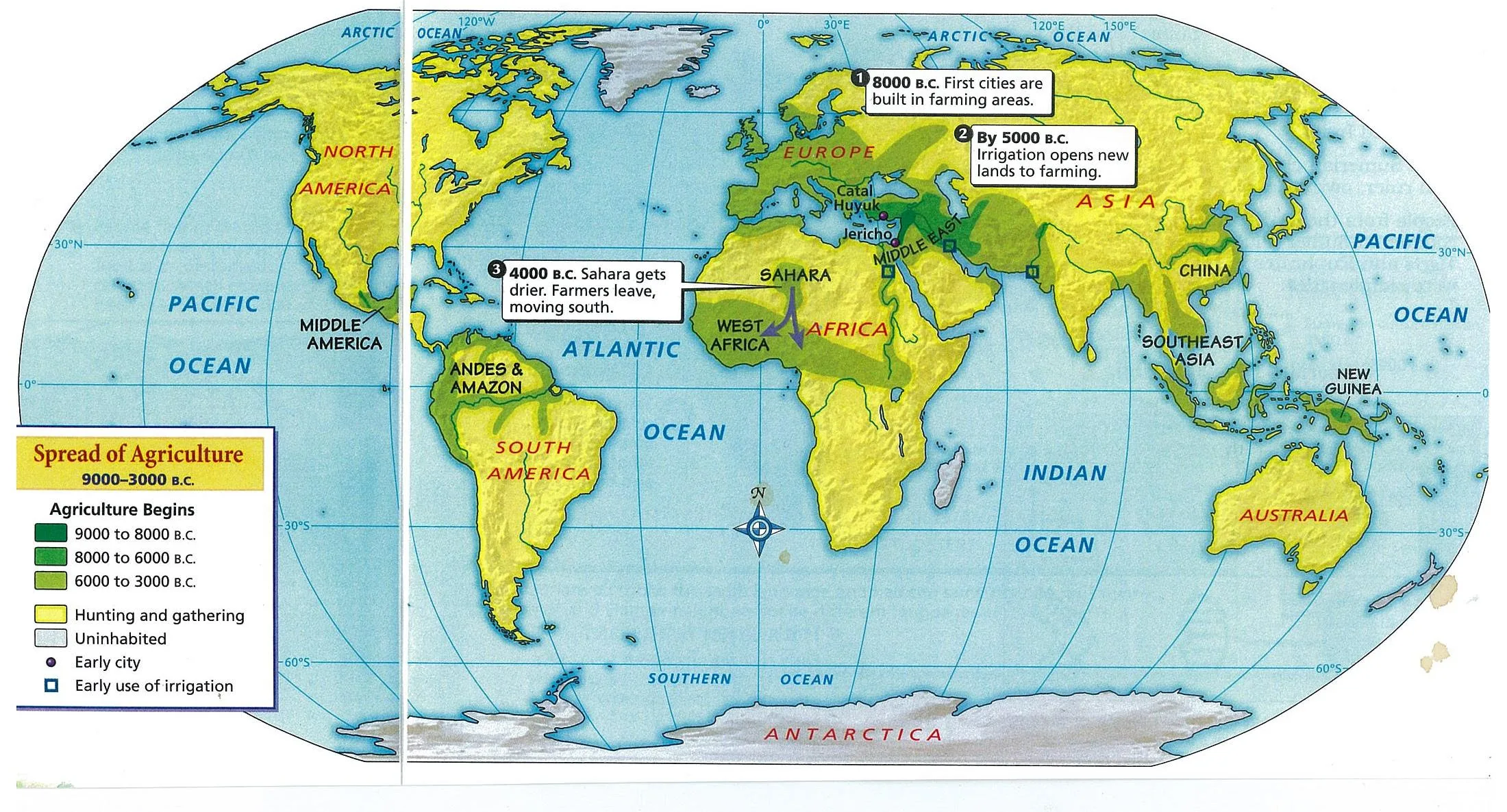
These civilizations and empires interacted with neighboring cultures and empires, such as Egypt, Anatolia, Syria, and Iran, leading to a rich exchange of ideas, trade, and cultural influences.
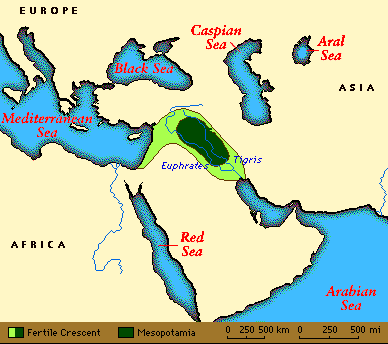
Mesopotamia holds immense historical significance as the birthplace of civilization. Its contributions to writing, mathematics, technology, and governance have shaped the world we live in today. The region’s diverse cultures and empires have left a lasting impact on human history, making Mesopotamia a fascinating subject of study and exploration.
Mesopotamia is also known for its ancient art, including the famous 4,300-year-old bronze mask of an Akkadian king, solid gold Sumerian harp, and numerous cuneiform tablets.
Fun Fact